Causes of hearing loss
Hearing loss can have many causes, including: exposure to loud environments, illness, earwax, aging, physical damage (such as a perforated eardrum or damage to the nerve endings inside the cochlea), or structural abnormalities in the ear itself.
Types of hearing loss
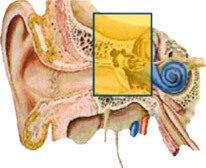
Conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss is often temporary and can be corrected. Conductive hearing loss stems from problems of the outer or middle ear and can be caused by:
- Infection
- Otosclerosis
- Build-up of wax or fluid
- Punctured eardrum
This type of hearing loss can be treated with wax removal, medicine, or surgery.
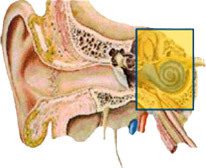
Sensorineural hearing loss / Nerve deafness
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type of hearing loss. In fact, it accounts for 90% of all adult hearing problems and is caused by aging and noise. With sensorineural hearing loss:
- There are problems with the cochlea and the auditory nerve.
- Sounds not only diminish in volume but also become distorted.
- High frequency sounds and some spoken words are first to go.
- Low frequency sounds, such as vowels, are heard better.
This type of hearing loss can be treated with amplification (hearing instruments) and, occasionally, surgery. For more information about surgical procedures, consult a physician.
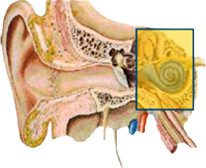
Mixed hearing loss
Both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss occur at the same time.
How can I prevent hearing loss?
The easiest way to prevent hearing loss is to avoid unprotected exposure to loud noises, which can damage the nerve endings inside the cochlea. Studies show that prolonged exposure to sounds at or above 90dB can damage your hearing. Sounds at this volume can come from vacuum cleaners, lawnmowers, chainsaws, or loud music. Always wear earplugs whenever your surroundings are so loud that you have to raise your voice to be heard.
Frequently Asked Questions
Over 14 million Canadians of all ages have some hearing impairment.
Hearing loss can happen at any age. It isn’t just an older person challenge. Typically signs of hearing loss can be measured as early as our 30s.
Hearing loss is as individual as you are. If you really want to hear the world to the best of your ability, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution.
